Table of Contents
ToggleX-Y recorders or X-Y plotters accept two inputs and create a chart or graph of one input versus the other. They are commonly used to determine the relationship between the two inputs.
It is one of the types of recording and indicating instrument. Let’s see what is recorder? and classification of recorders first.
Introduction to Recorders
- It is often necessary to have a permanent record of a phenomenon being investigated, e.g., in industrial & research processes, it is required to monitor continuously the condition, state, or value of the process variables such as flow, pressure, temperature, current, & voltage etc.
- A recorder, thus, records electrical/non-electrical quantities as a function of time.
- This record may be written/printed and later on can be examined & analyzed to obtain a better understanding and control of the process
- Currents/voltages can be recorded directly while non-electrical quantities are recorded indirectly by first converting them to equivalent currents/voltages with the help of sensors or transducers.
- Depending on how the data acquired is recorded? The recorders are classified as follow:
- Analog Recorders
When we are dealing with a wholly analog system, analog recorders are broadly classified into
- Graphic Recorders
- Oscillographic Recorders
- Magnetic-Tape Recorders
- Digital Recorder
For the system whose output is in digital form
Generally, graphic recorders are devices which display & store pen-and-ink record of the history of some physical event on a chart.
Basic Elements of Graphic Recorder
- Chart for displaying & storing the recorded information.
- A stylus or pen moving in proper relationship to paper/chart.
- A suitable means of Interconnection or Interface to couple the stylus to the source of information.
Graphic recorders may be classified into
- Strip chart recorders
- X-Y recorders
X-Y Recorder or X-Y Plotter
In X-Y recorder trace of the marking pen will be due to the combined effects of two signals applied simultaneously. It is an instrument which gives a graphic record of the relationship between two variables, i.e., one emf is plotted as a function of another emf.
With the help of these recorders and appropriate transducers, a physical quantity may be plotted against another physical quantity.
Construction
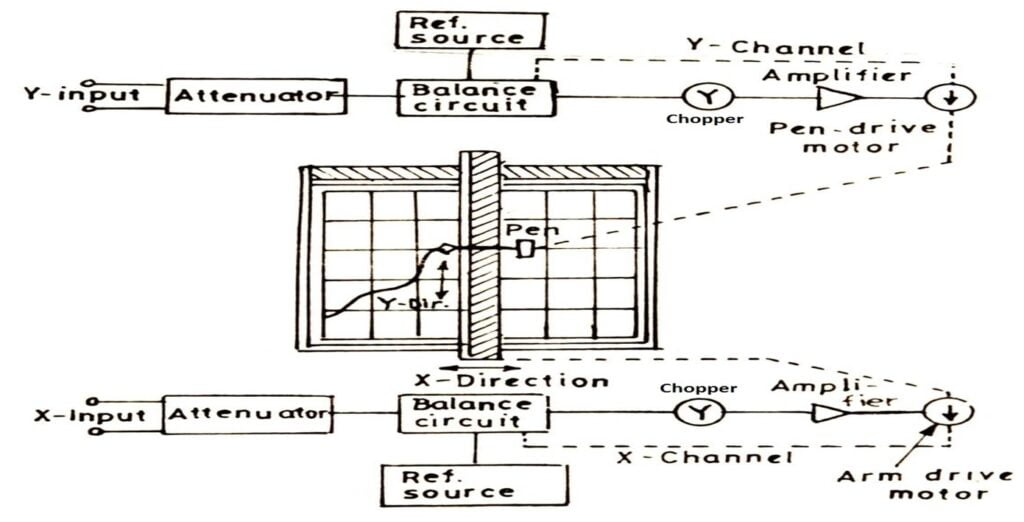
- Here, one self-balancing potentiometer circuit moves the recording pen in x-direction while another self-balancing potentiometer circuit moves the recording pen in y-direction and the paper remains stationary.
- An X-Y recorder consists of a pair of servo-systems, driving a stylus in two axes through a proper sliding pen and moving arm arrangement, with reference to a stationary paper chart.
Working
- A signal enters in each of the two channels.
- Attenuators are used to bring the input signals to the levels (full scale range: 0.5 mV) acceptable by the recorder.
- As shown in figure, error signals (the difference between the input signals and reference voltage) are fed to a chopper which convert dc signals to ac signals.
- The signals are then amplified in order to actuate servomotors which are used to balance the system and hold it in balance as the value of the quantity being recorded changes.
- The action described above takes place in both the axes simultaneously. Thus, we get a record of one variable w.r.t. another.
- In some X-Y recorders, one self-balancing potentiometer controls the position of the rolls (i.e. the paper) while another self-balancing potentiometer controls the position of the recording pen.
- An X-Y recorder may have a sensitivity of 10 µV/mm, a slewing speed of 1.5 m/s, a frequency response about 6 Hz for both axes, chart size of 250 x 180 mm, and accuracy of about ± 0.3%.
Advantages of X-Y Recorder
- The instantaneous relationship between two physical quantities can be recorded.
- The relationship between either electrical or non-electrical quantities can be recorded.
- In modem types of recorders, zero offset adjustments are available.
Applications of X-Y Recorder
- Speed-torque characteristics of motors
- Plotting of characteristics of vacuum tubes, Zener diodes, rectifiers, transistors etc.
- Pressure-volume diagrams for LC engines
- Pressure-flow studies for lungs
- Lift drag wind tunnel tests
- Regulation curve (output versus input voltage) of power supplies
- Electrical characteristics of materials such as resistance versus temperature
- Plotting stress versus strain curves, hysteresis curves etc.
Recent posts
Related posts:
- Industrial Computerized Tomography
- Measurement of Vibration
- Electrical Telemetry | Telemetry System
- Non-Destructive Thickness Measurement
- Humidity Measurement
- Smoke and Fire Detection | Heat and Smoke Detectors
- Thermal Conductivity Measurement
- Piezoelectric Transducer
- Signal Conditioning
- Transducer and Its Classification
- Selection Criteria of Transducer
- Strain Gauge
- LVDT Linear Variable Differential Transformer
- Hall Effect Transducer
- Photoelectric Transducers
- Light Sensors or Photosensors
- Resistance Temperature Detectors or Resistance thermometer
- Thermocouple
- Sensors and Transducers
- Thermistors
- Voltage and Current Telemetry System


Dear electronicsforyou.in webmaster, Thanks for the well-researched and well-written post!
Hi electronicsforyou.in admin, Thanks for sharing your thoughts!